Clinical Evidence
Explore the science behind Wholomics early cancer detection innovation.
At Wholomics, transparency and scientific rigor are at the core of what we do. This page is dedicated to showcase the research and clinical studies that drive our technology forward.
Publications & Evidence
Multi Cancer Early Detection - ASCO Annual Meeting 2025
Journal of Clinical Oncology (JCO)
May 2025
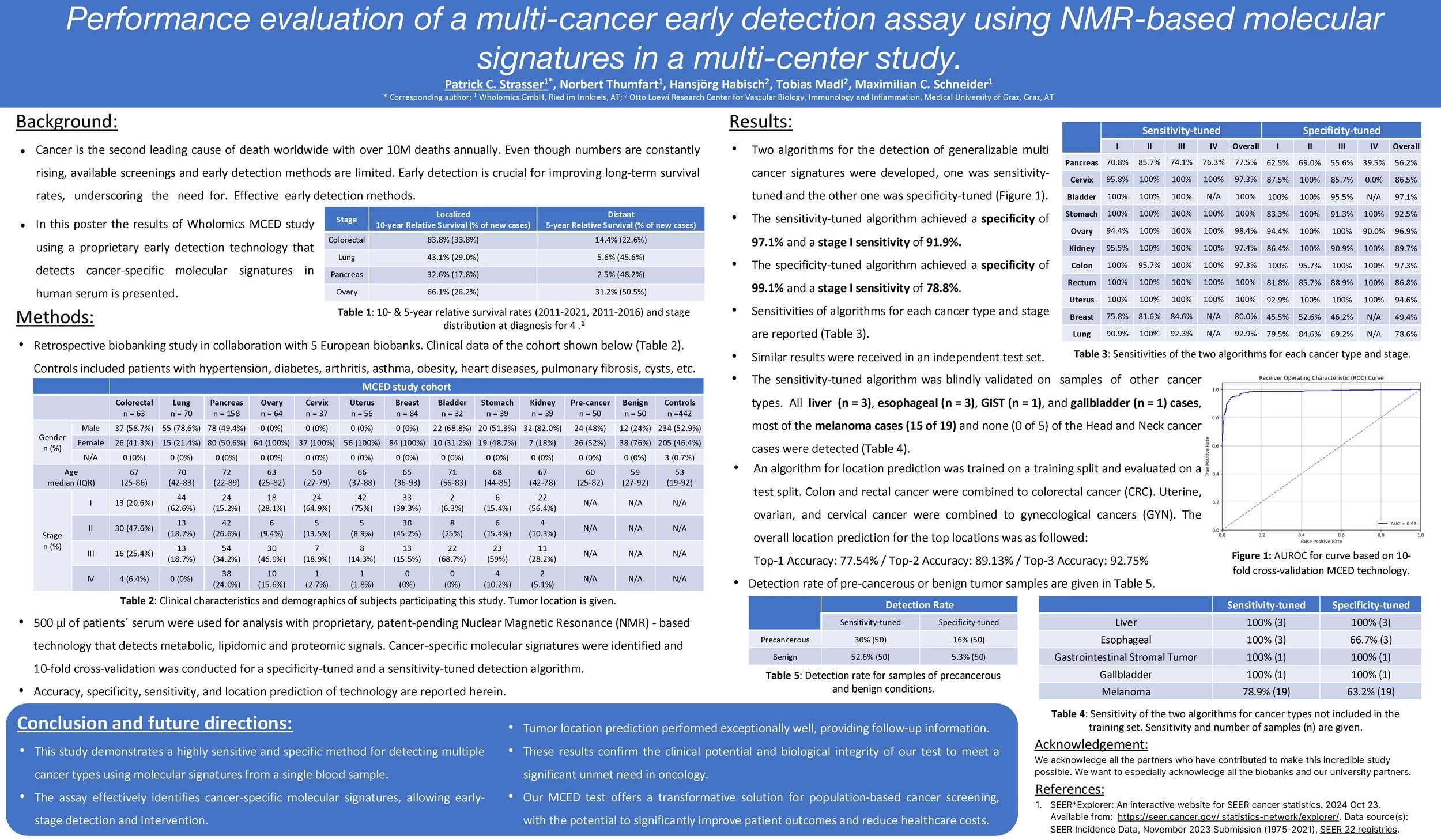
Wholomics MCED assay, powered by Wholomics’ proprietary NMR-based molecular signatures, represents a true leap forward in early cancer detection. At the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting, we presented results from a multi-center study with 1,211 participants, making this one of the most robust evaluations of a functional biomarker approach in early detection to date.
Key Highlights of the Study:
Broad Cohort: 1,211 samples across 13 cancer types (including colorectal, lung, pancreatic, ovarian, liver, gastric, renal, and more), 50 precancerous, 50 benign, and 442 controls.
Exceptional Accuracy: Wholomics MCED test achieved 91.8% overall sensitivity, 91.9% Stage I sensitivity, and 97.1% specificity.
Ultra-High Specificity Option: Specificity-tuned model delivered 99.1% specificity with 76.6% overall sensitivity.
Tumor Localization: Correctly identified the tumor site with 77.5% top-1 accuracy, rising to 92.8% in top-3 predictions.
This study marks a milestone in cancer diagnostics — for the first time, a non-DNA based, cost-efficient blood test has demonstrated such high accuracy for Stage I disease across multiple cancers. Wholomics is now expanding validation in prospective cohorts and working with partners to bring this breakthrough technology into real-world screening programs.
For a detailed insight into our research and findings, we invite you to download the poster published at the ASCO Annual Meeting 2025 in Chicago. This poster encompasses the methodology, results, and implications of our study, highlighting our commitment to combating solid cancers through early detection.
Article Citation:
Patrick C. Strasser et al., Performance evaluation of a multi-cancer early detection assay using NMR-based molecular signatures in a multi-center study.. JCO 43, e15079-e15079(2025). DOI:10.1200/JCO.2025.43.16_suppl.e15079
Blinded Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection - ASCO Annual Meeting 2024
Journal of Clinical Oncology (JCO)
May 2024
Independent blinded validation of a novel blood-based early pancreatic cancer detection test.
Wholomics pancreatic cancer early detection test was validated in an independent validation cohort. This confirms the clinical accuracy and reliability of Wholomics technology. The groundbreaking results mark a significant advancement in identifying this challenging disease in its earliest stages. This clinical study included around 400 patients with pancreatic cancer, with a focus on early-stage detection, non-cancerous controls harboring common diseases, like diabetes, arthritis, and neurodegenerative diseases as well as patients with precancerous and benign pancreatic conditions.
Key Highlights of the Study:
Participant Demographics: 394 individuals including pancreatic cancer patients, non-cancerous controls and those with precancerous and benign pancreatic diseases.
Accuracy: Reached ~92.5% overall accuracy in distinguishing PDAC patients from controls.
Sensitivity & Specificity: Achieved 91.7% sensitivity and 95.0% specificity in the blinded validation cohort.
Early Detection: Strong performance even in early-stage disease, demonstrating the ability to detect pancreatic cancer well before it progresses to late stages.
This study represents a critical step in our efforts to improve early detection rates for pancreatic cancer, potentially leading to better patient outcomes and survival rates.
For a detailed insight into our research and findings, we invite you to download the poster we presented at the ASCO Annual Meeting 2024 in Chicago. This poster encompasses the methodology, results, and implications of our study, highlighting our commitment to combating pancreatic cancer through early detection.
Article Citation:
Patrick Christian Strasser et al., Independent blinded validation of a novel blood-based early pancreatic cancer detection test. JCO 42, 4166-4166(2024). DOI:10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.4166
Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection -
ASCO GI Symposium 2024
Journal of Clinical Oncology (JCO)
January 2024
A novel early cancer detection approach for pancreatic cancer.
Wholomics pancreatic cancer early detection test was evaluated on a clinical cohort from the UMC Amsterdam. This marks a significant advancement in identifying this challenging disease in its earliest stages. The clinical study included 104 participants, carefully balanced between healthy controls and individuals diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, with a focus on early-stage detection. The study also included patients with precancerous conditions, providing a comprehensive understanding of the disease's progression.
Key Highlights of the Study:
Participant Demographics: The study comprised 104 individuals, split between healthy controls, pancreatic cancer patients, and patients with chronic pancreatitis.
Accuracy: Reached ~99.1% accuracy in differentiating chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer patients from healthy controls and ~95.2% accuracy in distinguishing pancreatic cancer patients from chronic pancreatitis patients.
Sensitivity & Specificity: Achieved 100.0% sensitivity and 98.0% specificity for differentiating patients with pancreatic diseases from healthy patients.
Focus on Early Detection: Emphasis on identifying pancreatic cancer in its early stages, crucial for effective treatment and outcomes.
Inclusion of Precancerous Conditions: Analysis of patients with precancerous conditions to enhance understanding of early cancer development.
This study represents a critical step in our efforts to improve early detection rates for pancreatic cancer, potentially leading to better patient outcomes and survival rates.
For a detailed insight into our research and findings, we invite you to download the poster we presented at the ASCO GI Symposium 2024 in San Francisco. This poster encompasses the methodology, results, and implications of our study, highlighting our commitment to combating pancreatic cancer through early detection.
Article Citation:
Maarten F. Bijlsma et al., A novel early cancer detection approach for pancreatic cancer. JCO 42, 613-613(2024). DOI:10.1200/JCO.2024.42.3_suppl.613
Minimal Residual Diseases Monitoring
The Monitoring Project at Wholomics represents a crucial advancement in the ongoing care of cancer patients. Currently in the planning phase, this project has embarked on its first pilot study in collaboration with European Biobanks. The focus is on longitudinal sample collection and analysis from cancer patients, providing valuable insights into the progression and recurrence of the disease.
Key Highlights of the Monitoring Project:
Longitudinal Study Design: Focusing on the collection and analysis of samples over time to monitor cancer progression.
Pilot Study Phase: The initial phase involves a pilot study, currently in the stage of analyzing the first set of samples.
Targeting Unmet Needs in Monitoring: This project aims to offer an effective monitoring solution for patients where traditional tumor markers are either not applicable or lack sufficient accuracy.
The ultimate goal of the Monitoring Project is to provide a more reliable, continuous monitoring system for cancer patients, especially those for whom current methods fall short. This could revolutionize how we track cancer progression and response to treatment, ultimately leading to more personalized and effective care strategies.
We invite collaborations from researchers, healthcare institutions, and biobanks who share our vision of enhancing cancer patient monitoring. If you are interested in participating in this pioneering study or would like more information, please contact us. Your involvement could make a significant difference in the lives of cancer patients worldwide.
Precision Oncology
The Therapy Response Prediction Project at Wholomics is a forward-thinking initiative aimed at enhancing personalized medicine in cancer care. This project, currently in the planning phase, has launched its first pilot study in partnership with European Biobanks. It focuses on developing a methodology to predict how individual patients might respond to common cancer treatments, laying the groundwork for personalized treatment plans and companion diagnostics.
Key Highlights of the Therapy Response Prediction Project:
Pilot Study in Progress: We are in the early stages of this project, currently analyzing the initial set of samples collected.
Personalized Medicine Focus: The project's goal is to develop tools that can predict individual responses to various cancer therapies, enabling more tailored and effective treatment plans.
Companion Diagnostics Development: A significant aim of the project is to create companion diagnostics that can guide therapy choices based on predicted responses.
The objective of this project is to offer a prediction model for therapy responses, which could significantly improve treatment outcomes for cancer patients by personalizing their treatment plans, ultimately steering the future of oncology towards more effective, individualized treatment regimens..
If you would like to contribute to this groundbreaking project or need more information, please reach out to us. Your involvement can help us change the landscape of cancer treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Become a Partner
Wholomics is considering select clinical partners.
Fill out the form below and one of our staff members will get back to you. .